-
Research Highlight
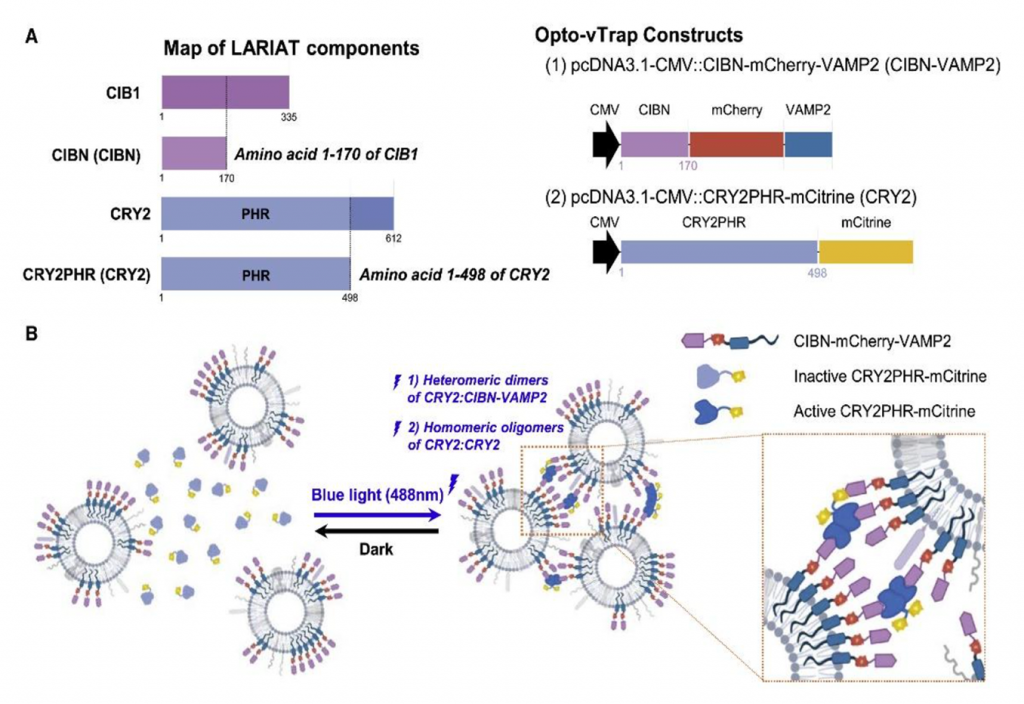
Opto-vTrap, an optogenetic trap for reversible inhibition of vesicular release, synaptic transmission, and behavior
Spatiotemporal control of brain activity by optogenetics has emerged as an essential tool to study brain function. To silence brain activity, optogenetic probes, such as halorhodopsin and archaerhodopsin, inhibit transmitter release indirectly by hyperpolarizing membrane potentials. However, these probes cause an undesirable ionic imbalance and rebound spikes. Moreover, they are not applicable to use in non-excitable glial cells. In this study we engineered Opto-vTrap, a light-inducible and reversible inhibition system to temporarily trap the transmitter-containing vesicles from exocytotic release. Light activation of Opto-vTrap caused full vesicle clusterization and complete inhibition of exocytosis within 1min, which recovered within 30 min of light off. We found a significant reduction in synaptic and gliotransmission upon activation of Opto-vTrap in acute brain slices. Opto-vTrap significantly inhibited hippocampus-dependent memory retrieval with full recovery within an hour. We propose Opto-vTrap as a next-generation optogenetic silencer to control brain activity and behavior with minimal confounding effects....read more

291 Daehak-ro Yuseong-gu Daejeon, 34141, Republic of Korea
Partnered with KAIST Breakthroughs and KAIST Compass