-
Research Highlight Top Story
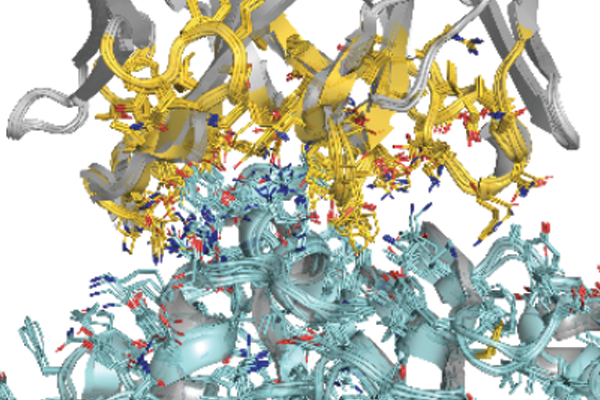
Computational design of a neutralizing antibody against all SARS-CoV-2 variants
Prof. Oh’s group has developed a neutralizing antibody against SARS-CoV-2 by computational method. The antibody binds to all SARS-CoV-2 variants, including Omicron, with pico- to femto-molar binding affinity....read more
-
Research Highlight
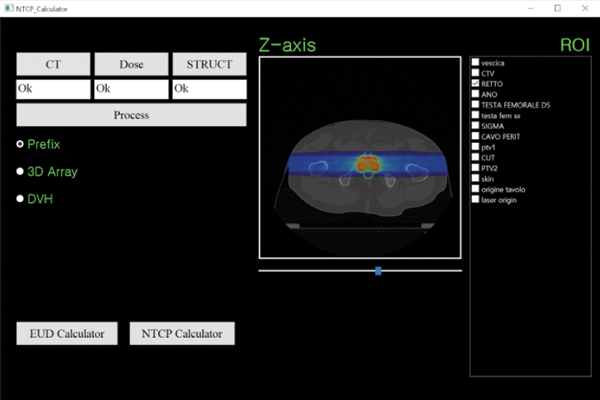
Normal tissue complication probability (NTCP) calculator development for research and clinical activities
Radiation therapy is one of the most important tools in the fight against cancer. Generally, tumor control is mainly considered for treatment planning. However, radiation-induced side effects are considered as well. The NTCP is the probability of critical normal tissue having complications as calculated from the combined effect of the radiation dose and volume. Some normal tissue complications are very important for a normal quality of life after radiation therapy. The NTCP calculator is software developed at KI IT Convergence to calculate the NTCP with various methods in a clinical format, DICOM. The Lyman-Kutcher-Burman NTCP model is implemented with a flexible parameter input interface. The NTCP calculator will be used at local university hospitals for research and clinical purposes....read more
-
Research Highlight
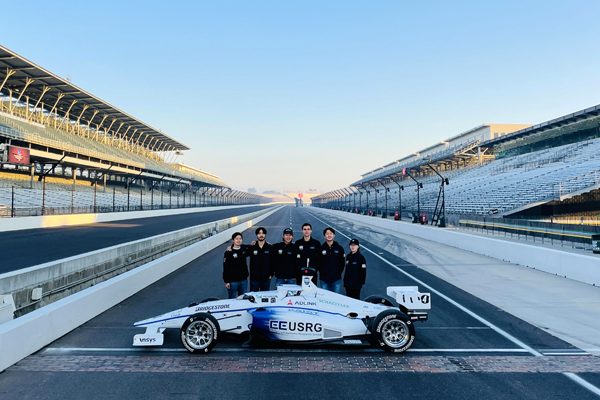
KAIST Racing Team finished as a semi-finalist in CES 2022 Autonomous Racing
Researchers at KI Robotics entered CES 2022 Autonomous Racing using their Indy AV-21 autonomous vehicle and competed with the world’s top researchers. Our team developed a cutting-edge autonomous racing software stack from scratch and successfully finished the race as a semi-finalist, only to lose to the top European teams....read more
-
Research Highlight
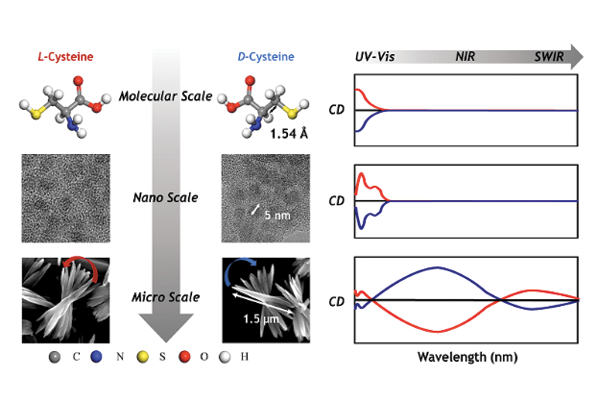
New chiral ceramic nanostructures: Broad chiroptical activity from ultraviolet (UV) to short-wave infrared (SWIR)
Prof. Yeom’s group has developed new chiral nanostructures with broad chiroptical activity from the UV to the SWIR region to expand the choice of material platforms. ...read more
-
Research Highlight
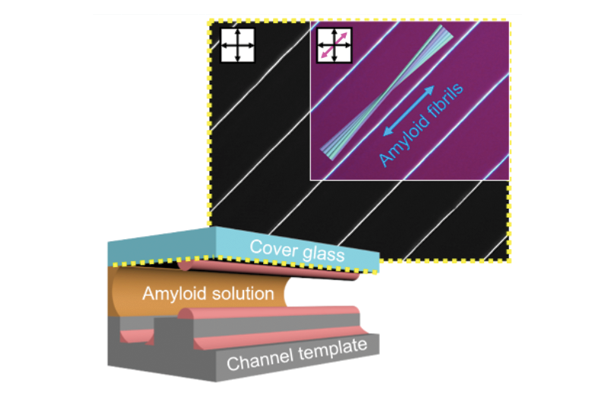
Fibril-to-Fiber Structure: Hierarchically Fabricated Amyloid Fiber via Evaporation-induced Self-assembly
Prof. Yoon’s group has suggested a facile way to produce protein-based amyloid aggregates, allowing long-range orientational and positional order. Using evaporation-induced self-assembly, a rationalized hierarchical structure will open new opportunities for developing novel functional biomaterials....read more
-
Research Highlight
Tomographic measurement of dielectric tensors at the optical frequency
Prof. YongKeun Park’s group has developed a label-free tomographic method for measuring and reconstructing 3D dielectric tensors, which have not been directly measured thus far. ...read more
-
Research Highlight
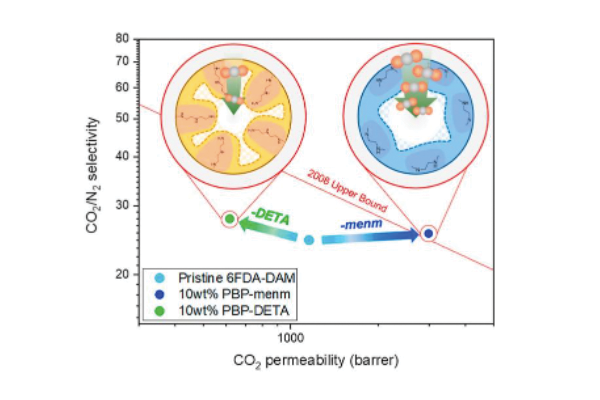
Effective functionalization of porous polymer fillers to enhance the CO2/N2 separation performance of mixed-matrix membranes
Prof. Bae’s group has developed a series of porous organic polymers possessing various functional groups, which were incorporated into an in-house polyimide to fabricate mixed-matrix membranes for CO2/N2 separation. Their systematic study revealed that both the structural properties and chemical functionality should be optimized together to obtained an ideal filler material for CO2-selective mixed-matrix membranes. The optimized membrane showed ultrahigh CO2 permeability of 2988 Barrers (158% higher than that of a pure polymer membrane) with a decent enhancement of the CO2/N2 selectivity....read more
-
Research Highlight
A Study of the Transformation of the Bio-health Industry in Daejeon based on AI/Big Data
KAIST KPC4IR collaborated with the Daejeon Institute for S&T Enterprise and People (DISTEP) and the European Commission Joint Research Center (EC JRC) for a study which aims to unlock AI, big data, and start-up ecosystems to revitalize the bio-health industry in Daejeon. Through this study, the center lays out a policy and strategy framework for bio healthcare transformation in Daejeon and in the Chungcheong provinces....read more
-
Research Highlight Top Story
High-speed autonomous driving is a game changer for future long distance travel.
Researchers at KI Robotics developed in-house autonomous driving solutions to participate in the world’s first high-speed autonomous racing competition at the prestigious Indianapolis Motor Speedway on October 23. ...read more
-
Research Highlight
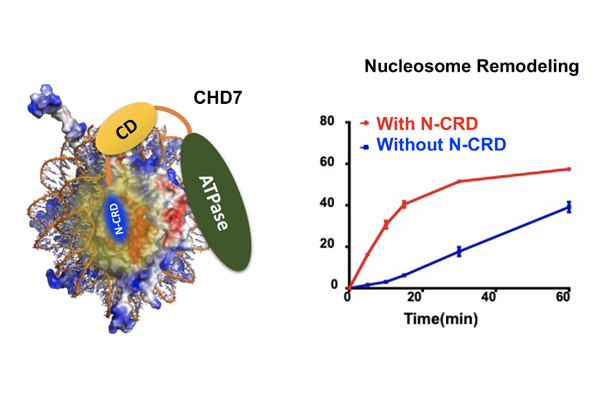
Revealing the molecular mechanism of a molecular motor controlling DNA high-order structure
Prof. J. Song's group has reveal how CHD7 molecular motor organizing DNA high-order structure is regulated by identifying a noble region in CHD7 combining an integrative structural biology approach. ...read more

291 Daehak-ro Yuseong-gu Daejeon, 34141, Republic of Korea
Partnered with KAIST Breakthroughs and KAIST Compass