Prof. Song’s group at the Department of Biological Sciences of KIB investigated the molecular mechanism of the CHD7 molecular motor, which utilizes ATP as an energy source to reorganize the DNA- high- order structure.
Chromodomain-Helicase DNA binding protein 7 (CHD7) is an ATP- dependent chromatin remodeler is involved in maintaining the open chromatin structure. Mutations of the CHD7 gene cause multiple developmental disorders, notably CHARGE syndrome. However, there is not much known about the molecular mechanism by which CHD7 remodels nucleosomes. Here, we conducted biochemical and biophysical analyses of the CHD7 chromatin remodeler and found that the N-terminal of the chromodomain (N-CRD) interacts with the nucleosome and contains a highly conserved arginine stretch, which is reminiscent of an arginine anchor.
Importantly, this region is required for the efficient ATPase stimulation and nucleosome remodeling activity of CHD7. Furthermore, a smFRET analysis shows mutations in the N-CRD cause defects in the remodeling activity. Collectively, our results uncover the functional importance of a previously unidentified N-terminal region in CHD7 and suggest that multiple domains in the chromatin remodelers are involved in regulating their activities.
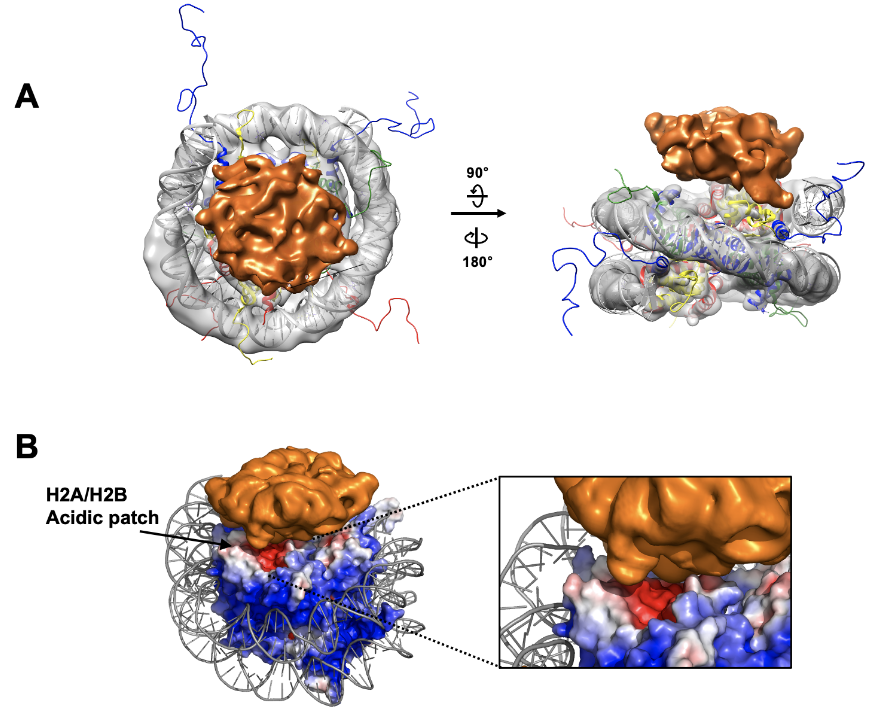
Cryo-EM map of N-CRD_Chromodomain bound to the nucleosome. The cryo-EM map for the nucleosome is shown in gray and the crystal structure of the nucleosome (1KX5) is docked in the map. The extra -density for the N-CRD_Chromodomain is shown in orange. The map was drawn at a contour 0.0057 for the nucleosome and 0.0021 for the N-CRD_Chromodomain.
Electrostatic surface representation of the nucleosome showing an acidic patch in contact with the cryo-EM density from the N-CRD_Chromodomain.
Dr. Eunhae Lee, Prof. Ji-Joon Song Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST
Homepage: http://www.song-kaist.org
E-mail: songj@kaist.ac.kr






