-
Research Highlight
Automatic Multi-Target Detection and Tracking for Unmanned Surface Vehicles
An algorithm for detecting and tracking multiple targets in marine environments was developed by a team of student researchers at KI-R. The algorithm was applied to an 8-m long unmanned surface vehicle and its performance was demonstrated in field tests in a real-sea environment....read more
-
Research Highlight
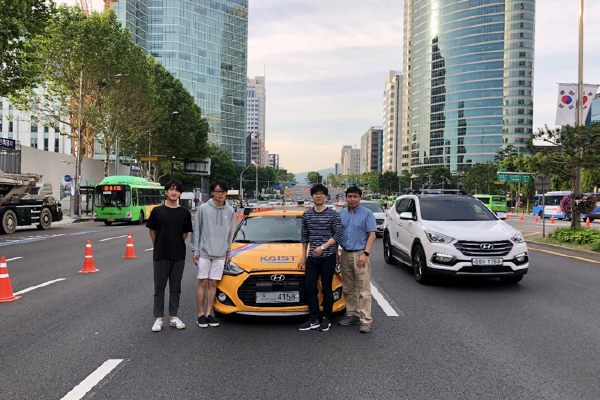
Research and Development of AI-powered Autonomous Cars in Seoul for Smart Cities
Professor Hyunchul Shim’s automotive driving research team participated in a technology demonstration organized by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, Korea. The event was held on Yeongdong boulevard adjacent to COEX, Seoul on June 17th. ...read more
-
Research Highlight
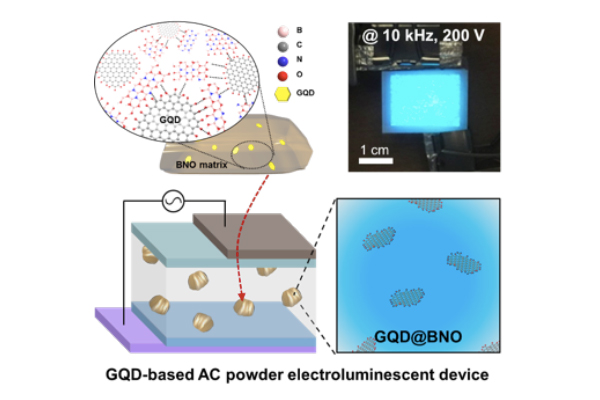
Bright Blue AC-Electroluminescence from Graphene Quantum Dots
Efficient solid-state photoluminescent graphene quantum dots embedded in boron oxynitride (GQD@BNO) was applied to AC powder electroluminescent device for the first time. ...read more
-
Research Highlight
High-Performance Electrochromic Devices from Two-Dimensional WO3 Nanosheets
Professor Seokwoo Jeon’s research team has developed a solution-phase synthesis method of two-dimensional WO3 nanosheets chemically converted from layered WS2 for the first time, to fabricate high-performance and robust electrochromic devices....read more
-
Research Highlight
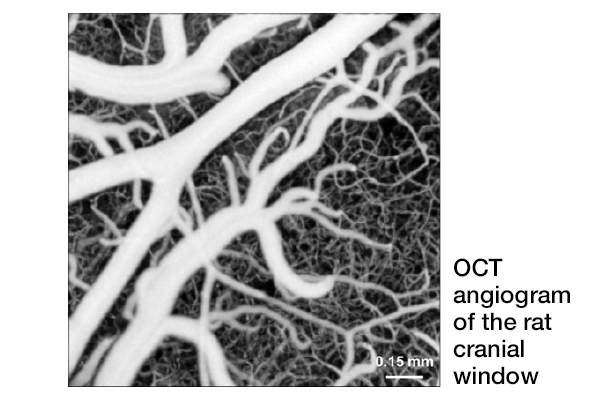
Quantitative hemodynamic analysis of cerebral blood flow and neurovascular coupling using optical coherence tomography angiography
Functional hyperemia in the rat cortex was investigated using high-speed optical coherence tomography (OCT) angiography. OCT angiography (OCTA) was performed to image the hemodynamic stimulus-response over a wide field of view. Temporal changes in vessel diameters in different vessel compartments were measured in order to monitor localized hemodynamic changes. This research demonstrates the potential of OCTA for the investigation of neurovascular coupling in small animal models....read more
-
Research Highlight
Deep learning for accelerated ultrasound imaging
To accelerate US imaging systems, Prof Jong Chul Ye’s team designed a deep learning technique that improved acquisition speed without compromising the image quality....read more
-
Research Highlight
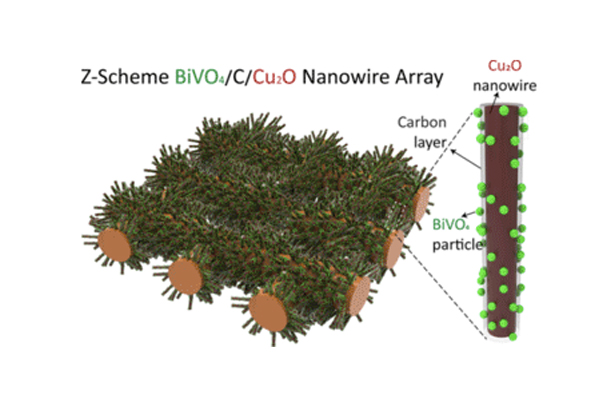
Three-Dimensional Nanostructured Z-scheme Photocatalyst for Carbon Dioxide Conversion
Efficient and stable CO2 conversion under visible light by using a novel photocatalyst with Z-scheme charge flow on 3-dimensional nanowire arrays....read more
-
Research Highlight
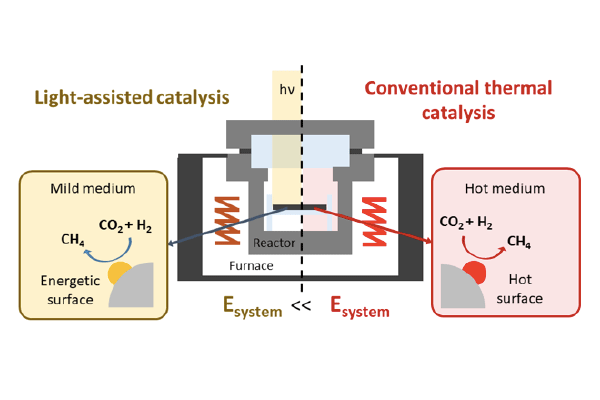
Energy-Saving CO2 Hydrogenation Using Light
Light-assisted CO2 hydrogenation produced methane on a Ru/SiO2 catalyst. By using both light and heat as an energy source, the total energy required for CO2 conversion could be reduced to 37%. The chemical reaction can be easily initiated or terminated by simply turning on or off the light....read more
-
Research Highlight
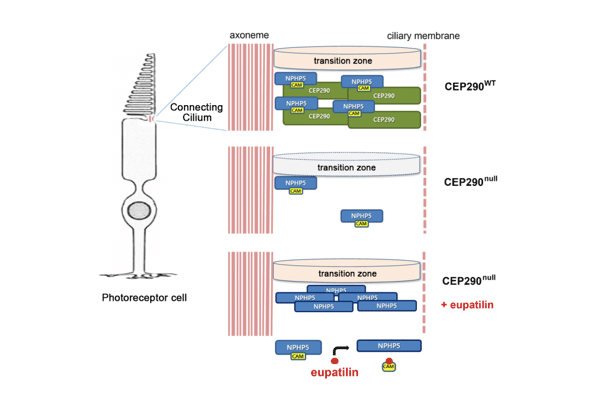
Drug discovery for ciliopathy, a rare genetic disorder
Ciliopathies are clinically overlapping genetic disorders involving structural and functional abnormalities of the cilia. CEP290, a gene mutated in several ciliopathies, encodes a protein that forms a complex with NPHP5 to support the function of the ciliary transition zone. In this study, the CRISPR/Cas9 system was used to generate a cell line model for CEP290-related ciliopathy, and cell-based chemical library screening identified eupatilin as a lead compound for developing ciliopathy medication. Eupatilin relieved ciliogenesis defects resulting from inactivation of the CEP290 gene. In rd16 mice harboring a blinding Cep290 in-frame deletion, eupatilin treatment improved both opsin transport to the photoreceptor outer segment and electrophysiological responses of the retina to light stimulation. The rescue effect was due to eupatilin-mediated inhibition of calmodulin binding to NPHP5, which promoted NPHP5 recruitment to the ciliary base. These results demonstrate that eupatilin rescues ciliary transition zone defects to ameliorate ciliopathy-related phenotypes....read more
-
Research Highlight
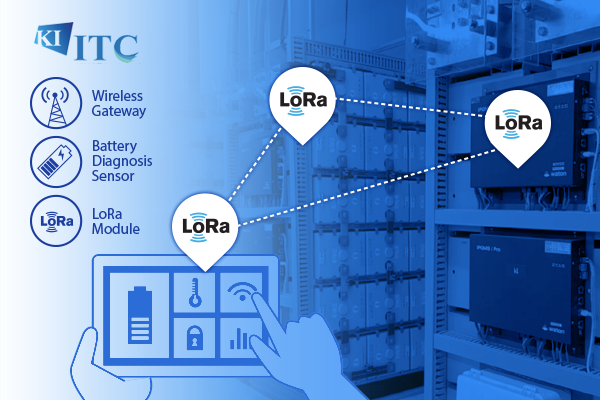
Development of web-based open low-power wireless power monitoring and diagnosis solution
At KAIST Institute for IT Convergence, professor Sung-Kwan Jung’s research team developed a LoRa based low-power wireless monitoring system for industrial battery diagnosis. They ultimately developed industrial wireless gateways with the IoT Edge Platform, two types of low-power wireless sensors, and LoRa modules for low-power wireless communications. They are now testing the results on a real industrial site....read more

291 Daehak-ro Yuseong-gu Daejeon, 34141, Republic of Korea
Partnered with KAIST Breakthroughs and KAIST Compass