-
Research Highlight
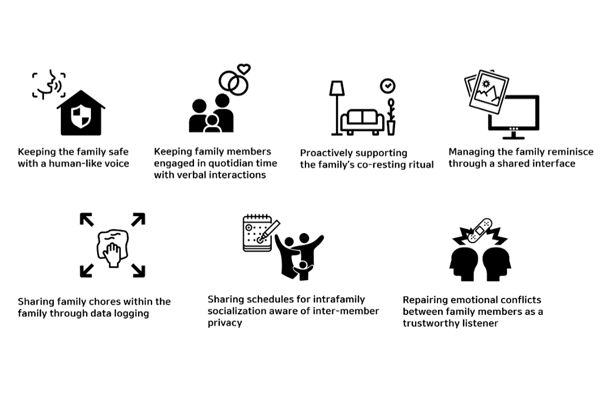
Investigating User Expectations on Roles of Family-shared AI Speakers
ID KAIST Researchers investigated the AI speaker as a family-shared technology and discovered its family-oriented roles for new design opportunities of AI speakers....read more
-
Research Highlight
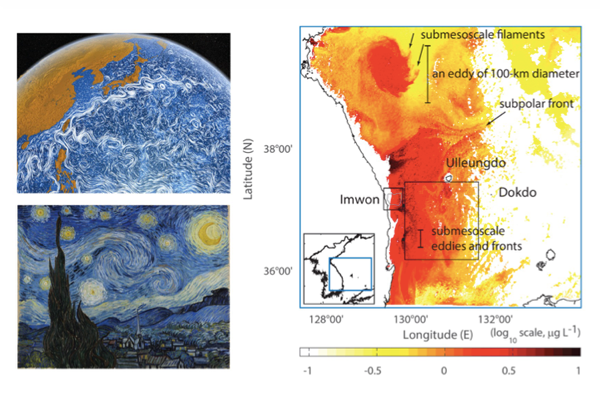
Quantification of Oceanic Energy Injection Scales and Elucidation of Primary Drivers Through Submesoscale Observations
Professor Sung Yong Kim and his team reported an injection spatial scale and primary driver in the oceanic submesoscale processes as O(10)-km scale baroclinic instability for the first time ever in the world through the ‘big data’ analysis of O(1) km and hourly surface current and chlorophyll concentration maps, observed by remote sensing instruments of high-frequency radars and geostationary ocean color imagery for at least one year up to five years. This work elucidates the pathways of oceanic energy cascades and will enhance studies of bio-physical interactions and improve the performance of regional and global climate models through realistic parameterization at submesoscale. The scientific outcomes have been published as two companion papers in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans, a prestigious, top-shelf journal in earth science and geophysical fluid dynamics....read more
-
Research Highlight
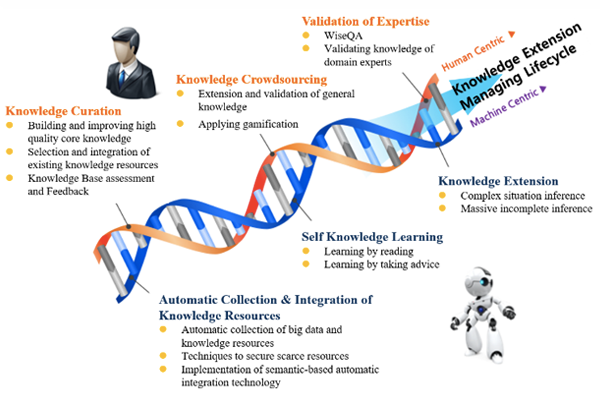
Development of Machine Reading Framework for Knowledge Base Population
The SWRC (Semantic Web Research Center, led by Prof. Choi) aims to construct and expand its knowledge base through self-machine-learning from unstructured big data (natural language), and to develop a novel technology to further verify the knowledge base....read more
-
Research Highlight
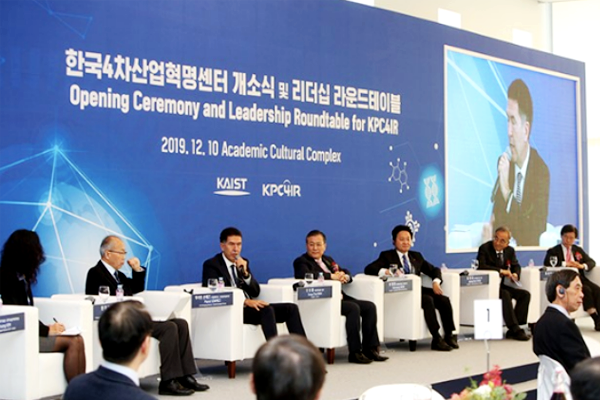
KAIST Launches the Korea Policy Center for the 4th Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) and Hosts a Leadership Round Table for 4IR.
KAIST opened the Korea Policy Center for the 4th Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR), an affiliate center of the World Economic Forum’s Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, on December 10, 2019....read more
-
Research Highlight
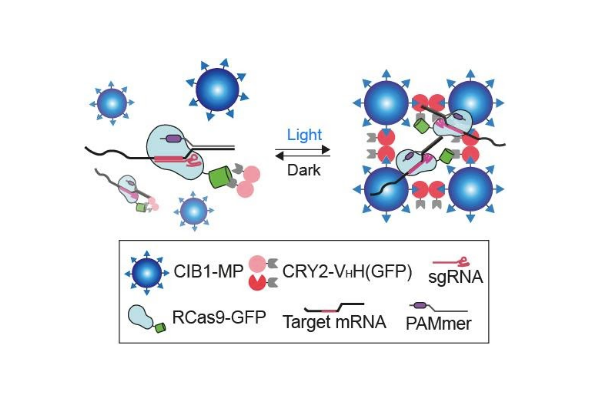
Optogenetic Control of mRNA Localization and Translation in Live Cells
A new optogenetic approach called mRNA-LARIAT enables the direct optogenetic control of localization and translation of specific mRNAs in living cells....read more
-
Research Highlight
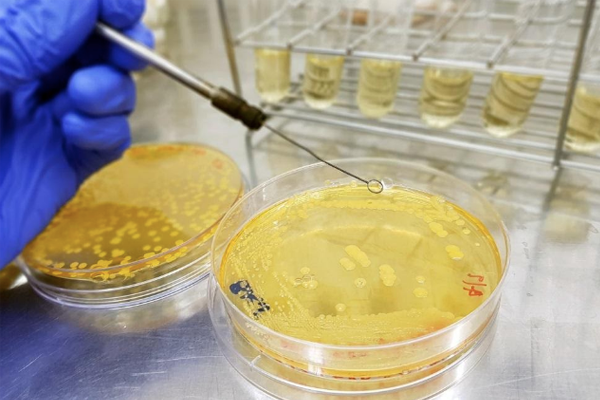
Engineering Bacteria to Produce Methyl-Anthranilate, a Grape Flavoring Compound
A direct fermentative approach to renewable methyl anthranilate (MANT) production from glucose is possible with metabolically engineered Escherichia coli and Corynebacterium glutamicum strains harboring a synthetic plant-originating metabolic pathway. This bio-based production platform will allow MANT, an important and widely used compound to impart grape scent and flavor, to be produced in a completely natural and sustainable manner....read more
-
Research Highlight
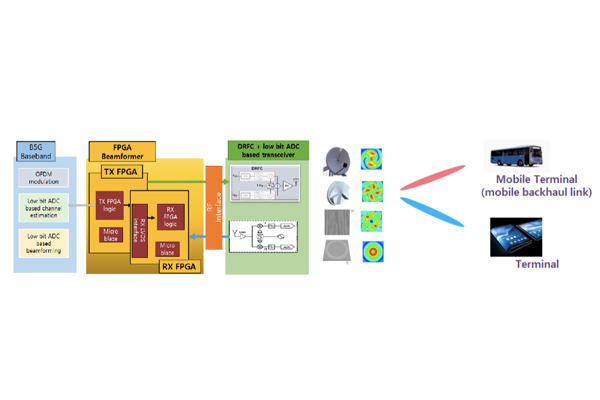
B5G and 6G Wireless Communication Technology
Fifth generation mobile communication technology has been commercialized around the 3.5 GHz band. If 5G technology that utilizes the 28 GHz millimeter band is commercialized, it will develop into a technology that drives the fourth industrial revolution. Prof. Ju Yong Lee is conducting research on B5G (Beyond 5G) mobile communication technology, centered on full digital technology. He is also conducting research on 6G mobile communication technology, which is expected to be commercialized around 2030. He is developing core technologies for antennas, RF frontends, and baseband modules in order to support 1 Tbps capacity for 6th generation mobile communication technology....read more
-
Research Highlight
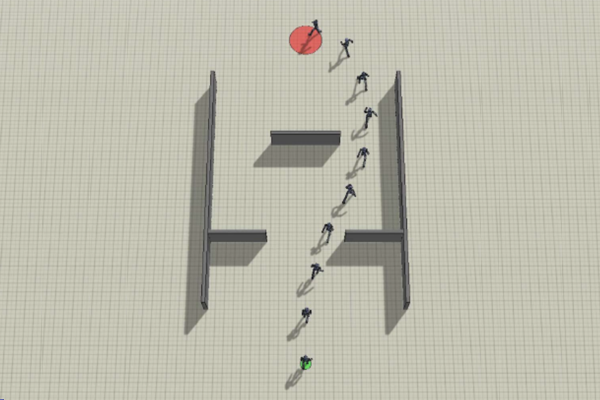
Self-Supervised Learning to Distill Hierarchy in High-Dimensional Dynamic Systems
Prof. Han-Lim Choi’s research team has developed a learning framework to control a high-dimensional robotic system that distills underlying hierarchical structure in robot motion data. By learning high-level intentions as well as low-level control actions, the proposed framework enables adaptation of policy learned from a certain task to much more diverse sets of tasks. ...read more
-
Research Highlight
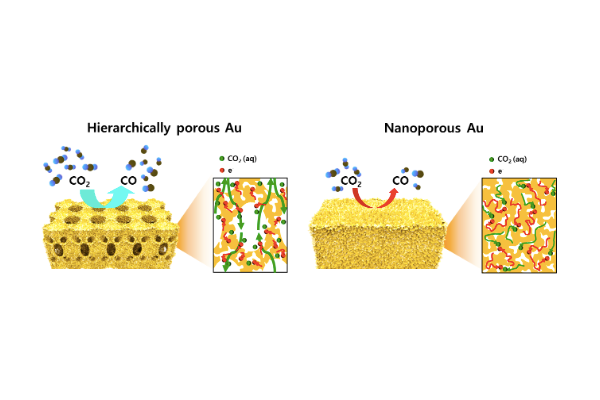
Development of New Class of Hierarchically Porous Au Electrocatalyst for Efficient Mass Transfer in CO2 Reduction Reaction
The team of Prof. Seokwoo Jeon and Prof. Jihun Oh developed a hierarchical nanostructured catalyst to reduce the use of gold via efficient mass transfer in CO2 reduction reaction....read more
-
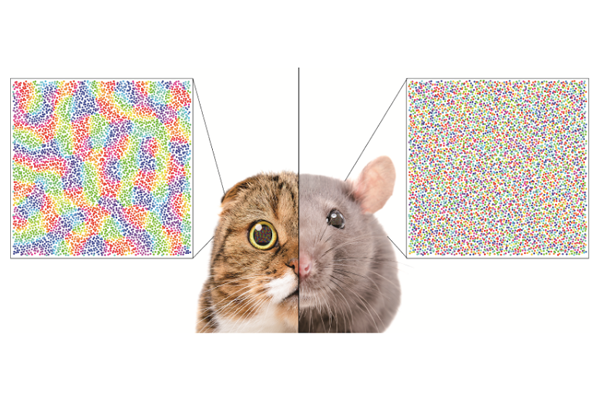
Research Highlight
Species-Specific Organization of Functional Circuits in Mammalian Visual Cortex
Theoretical model explains how visual cortexes develop uniquely across the brains of different mammalian species...read more

291 Daehak-ro Yuseong-gu Daejeon, 34141, Republic of Korea
Partnered with KAIST Breakthroughs and KAIST Compass