-
Research Highlight
Understanding the Preferred Driving-Style Guiding Experience in Autonomous Vehicles
ID KAIST researchers investigated the idea of user’s guidance of their preferred driving styles as a novel input channel for human-centric autonomous vehicle (AV) control....read more
-
Research Highlight
Reinforcement Learning Algorithm for Batch Chemical Process Control
Haeun Yoo, a member of Prof. Jay H. Lee’s group, has proposed a phase segmentation approach and modified deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm for batch process optimal control under uncertainty....read more
-
Research Highlight
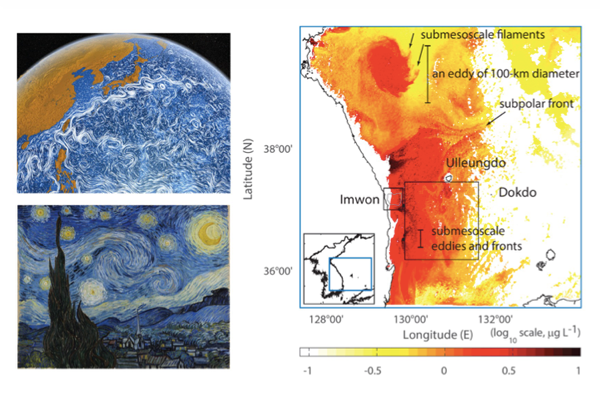
Quantification of Oceanic Energy Injection Scales and Elucidation of Primary Drivers Through Submesoscale Observations
Professor Sung Yong Kim and his team reported an injection spatial scale and primary driver in the oceanic submesoscale processes as O(10)-km scale baroclinic instability for the first time ever in the world through the ‘big data’ analysis of O(1) km and hourly surface current and chlorophyll concentration maps, observed by remote sensing instruments of high-frequency radars and geostationary ocean color imagery for at least one year up to five years. This work elucidates the pathways of oceanic energy cascades and will enhance studies of bio-physical interactions and improve the performance of regional and global climate models through realistic parameterization at submesoscale. The scientific outcomes have been published as two companion papers in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans, a prestigious, top-shelf journal in earth science and geophysical fluid dynamics....read more
-
Research Highlight
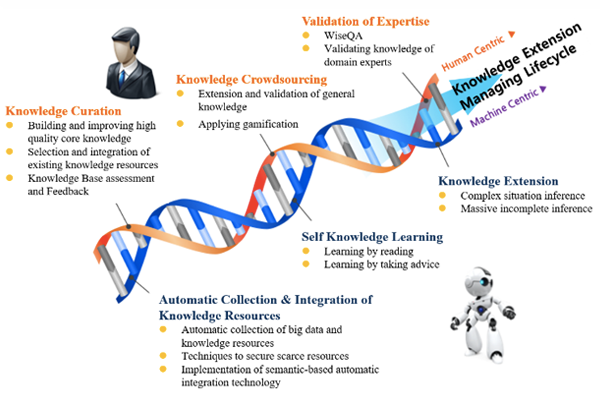
Development of Machine Reading Framework for Knowledge Base Population
The SWRC (Semantic Web Research Center, led by Prof. Choi) aims to construct and expand its knowledge base through self-machine-learning from unstructured big data (natural language), and to develop a novel technology to further verify the knowledge base....read more
-
Research Highlight Top Story
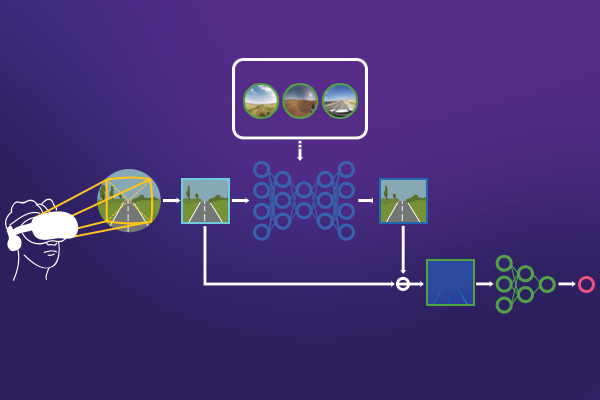
Development of VR Sickness Assessment Deep Network Considering Exceptional Motion for VR Video
Viewing safety is one of the main issues in viewing virtual reality (VR) content. In particular, VR sickness can occur when watching immersive VR content. To deal with viewing safety for VR content, objective assessment of VR sickness is of great importance. In this work, based on a deep generative model, we propose a novel objective VR sickness assessment (VRSA) network to automatically predict VR sickness. The proposed method takes into account motion patterns of VR videos in which exceptional motion is a critical factor inducing excessive VR sickness in human motion perception. The proposed VRSA network consists of two parts, the VR video generator and VR sickness score predictor. For the evaluation of VRSA performance, we performed comprehensive experiments with 360° videos (stimuli), corresponding physiological signals, and subjective questionnaires. We demonstrated that the proposed VRSA achieved a high correlation with human perceptual score for VR sickness....read more
-
Research Highlight
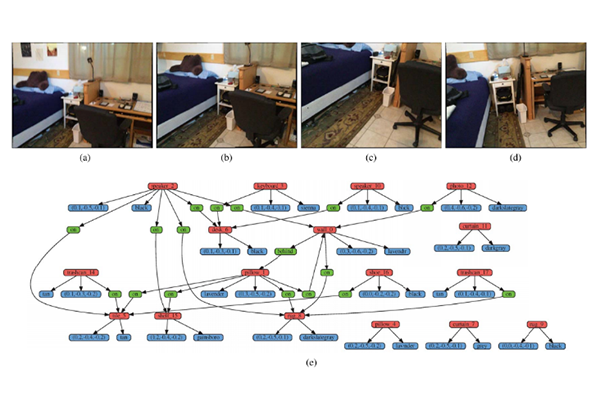
3-D Scene Graph: A Sparse and Semantic Representation of Physical Environments for Intelligent Agents
Professor Jong-Hwan Kim’s research team defined a 3-D scene graph, which represents physical environments in a sparse and semantic way....read more
-
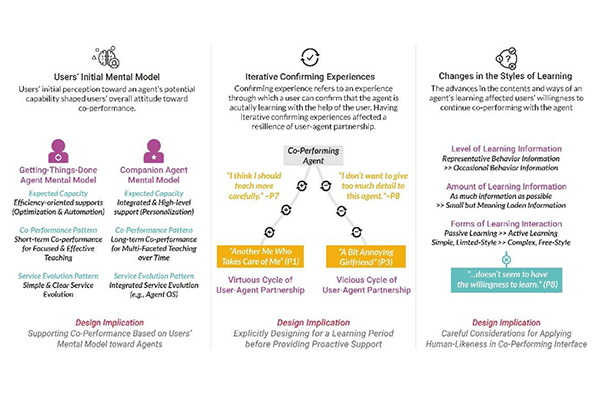
Research Highlight
Design for Building User-Agent Partnership in AI Assistant’s Learning and Adaptive Services
ID KAIST Researchers investigated how to design an intelligent assistant that can co-evolve with its user to be able to provide meaningful and effective personalized services....read more
-
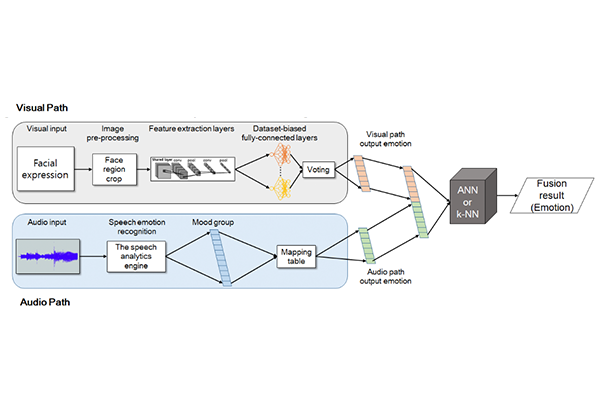
Research Highlight
Decision-Level Fusion Method for Emotion Recognition using Multimodal Emotion Recognition Information
We confirmed which combination of features of multi-modal emotion recognition achieves the highest accuracy....read more

291 Daehak-ro Yuseong-gu Daejeon, 34141, Republic of Korea
Partnered with KAIST Breakthroughs and KAIST Compass