-
Research Highlight
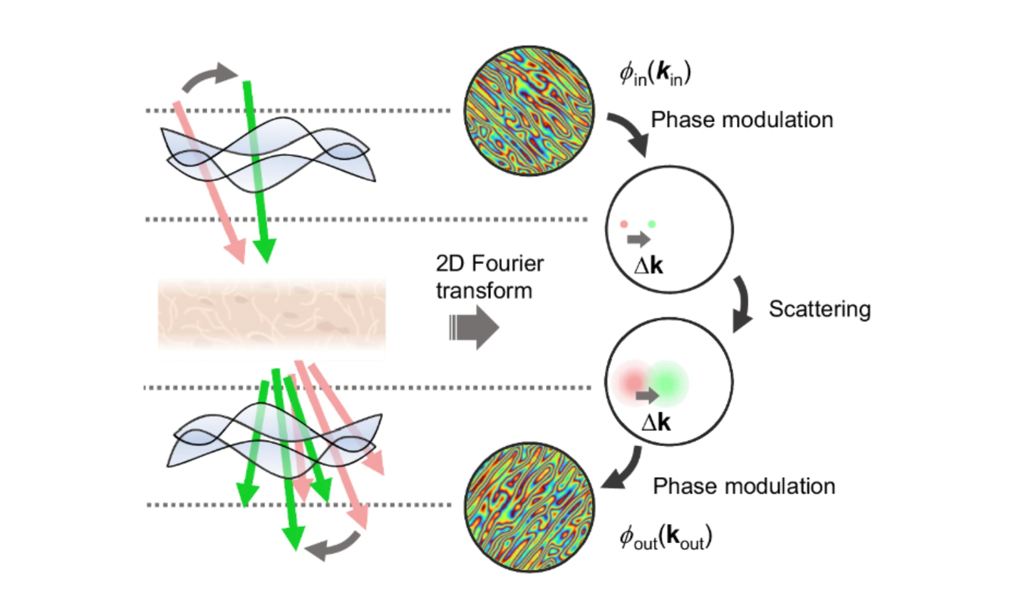
Digital aberration correction for enhanced thick tissue imaging exploiting a aberration matrix and tilt-tilt correlation from the optical memory effect
KAIST researchers develop high-resolution label-free imaging technology for thick biological tissues...read more
-
Research Highlight
In Situ Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Therapy by Local Delivery of an mRNA Encoding Membrane-Anchored Anti-CD3 Single-Chain Variable Fragment
Prof. Park’s group developed mRNA-LNPs to engineer macrophages and cancer cells in solid tumors for in situ TIL therapy, demonstrating significant antitumor effects. ...read more
-
Research Highlight
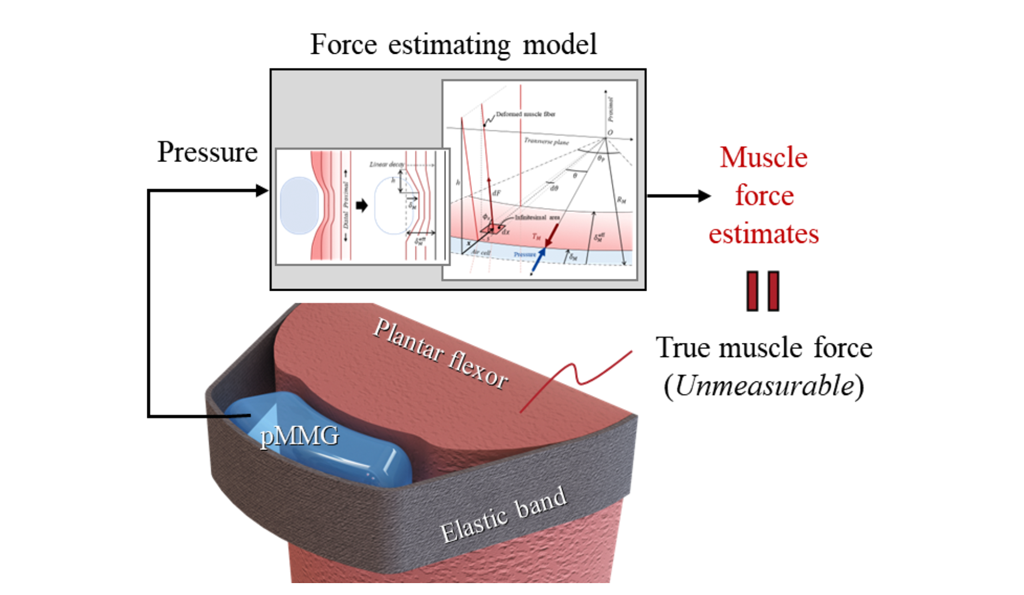
Plantar Flexion Muscle Force Estimation with a Soft Wearable Pneumatic Sensor System
Prof. Kong’s group developed a wearable pressure sensor for real-time estimation of plantar flexion muscle force by modeling intramuscular pressure....read more
-
Research Highlight
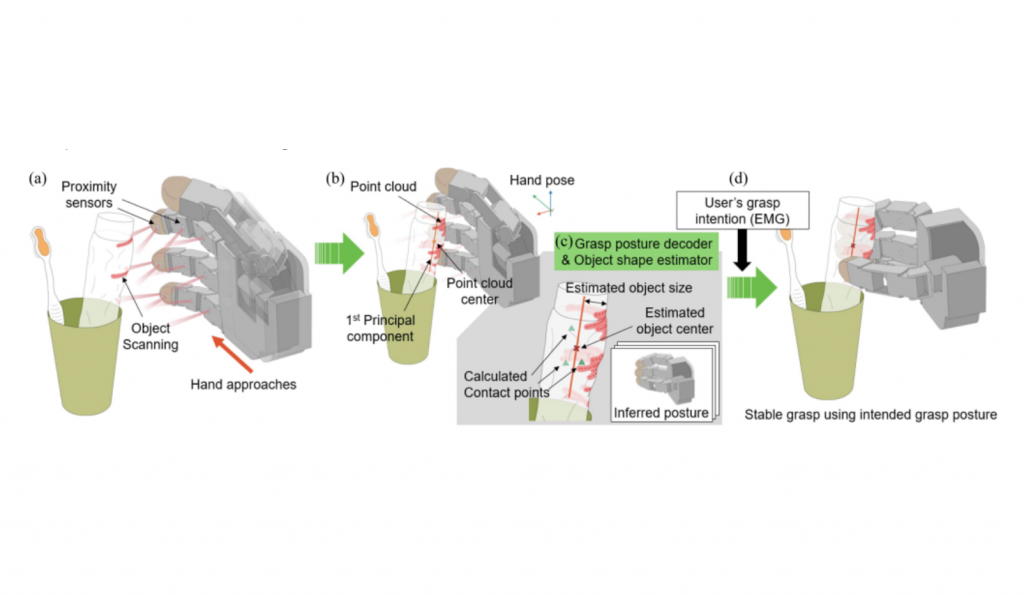
Proximity Perception-Based Grasping Intelligence: Toward the Seamless Control of a Dexterous Prosthetic Hand
A novel perception system, the proximity perception-based grasping intelligence (P2GI) system, has been developed to enhance the dexterity of prosthetic hands, closely mimicking human hand functionality. Utilizing embedded proximity sensors and a real-time decision-making algorithm, the P2GI system accurately maps the point cloud of an object and infers the user’s intended grasp posture, achieving a high accuracy of grasp posture classification and a high rate of task success. This advancement promises significant improvements in prosthetic hand control, potentially broadening the application of highly dexterous prosthetic hands in everyday tasks....read more
-
Research Highlight
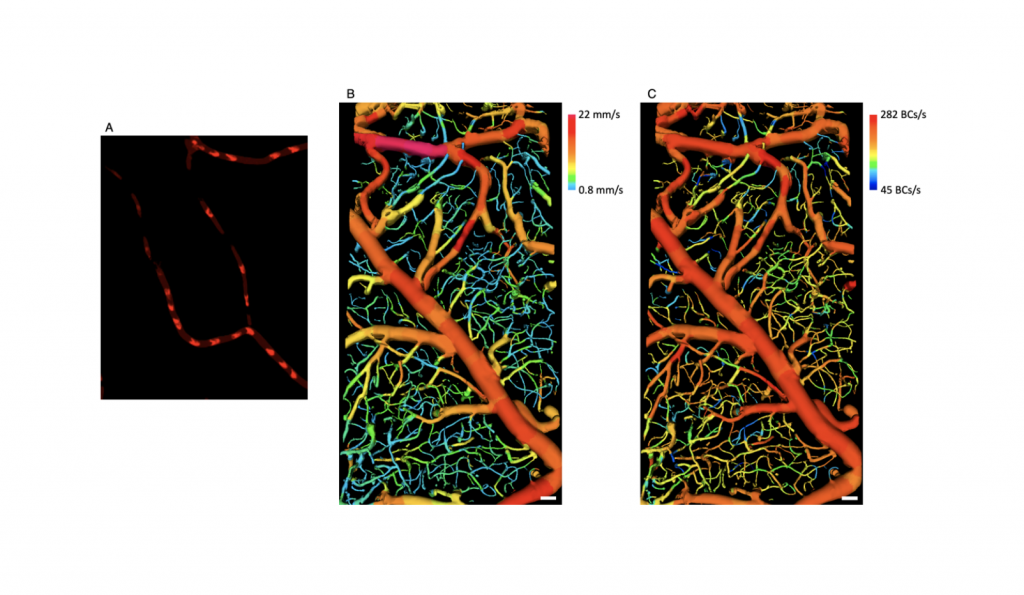
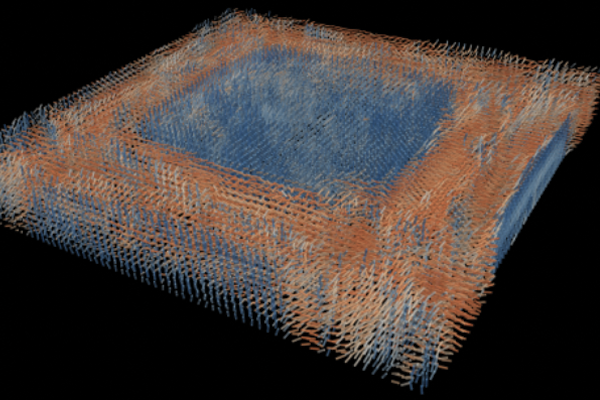
Direct Blood Cell Flow Imaging in Microvascular Networks
Prof. Wang-Yuhl Oh’s group has developed, for the first time, an imaging technology that visualizes blood cells flowing in complex three-dimensional vascular networks without using any contrast agent. ...read more
-
Research Highlight Top Story
High-resolution quantitative X-ray phase nanoimaging based on cutting-edge optical imaging methods
Prof. Park’s group has developed a novel high-resolution quantitative X-ray phase imaging system that can overcome two long-standing challenges in X-ray nanoimaging: the limitations in image resolution and the instability of phase retrieval methods. They applied optical imaging techniques that they have recently developed in the same group. The imaging systems have been successfully tested in both synchrotron source and X-ray free-electron laser facilities at Pohang Accelerator Laboratory....read more
-
Research Highlight
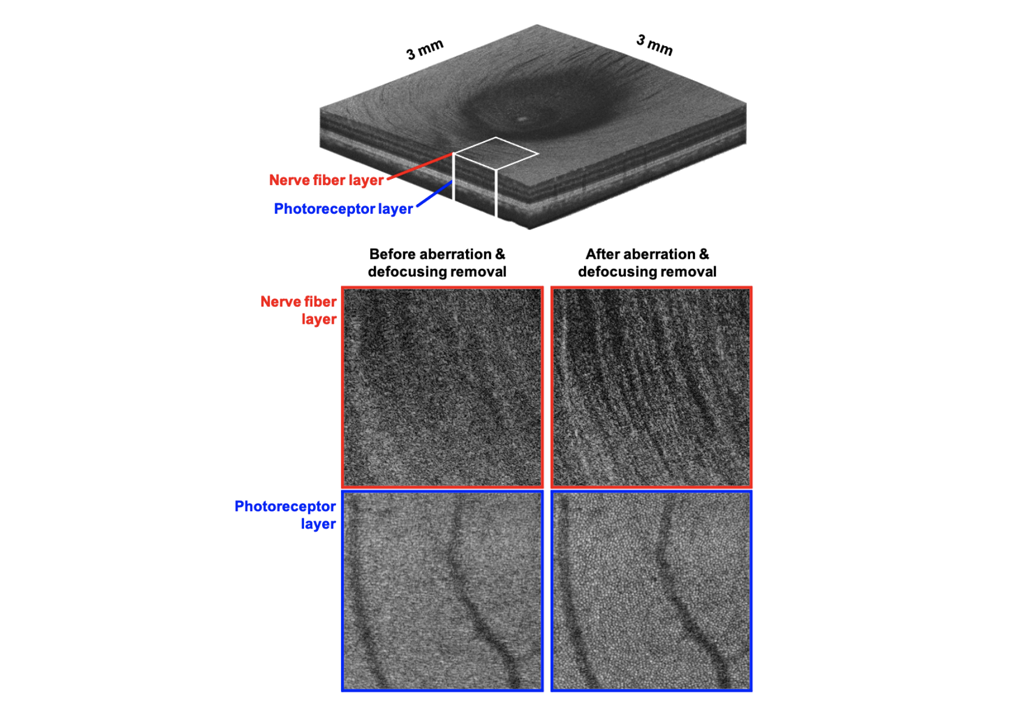
Wide-Field Three-Dimensional Depth-Invariant Cellular-Resolution Imaging of the Human Retina
Prof. Wang-Yuhl Oh’s group has developed, for the first time, a cellular-resolution imaging technology in a wide field human retina at all three-dimensional locations....read more
-
Research Highlight
Tomographic measurement of dielectric tensors at the optical frequency
Prof. YongKeun Park’s group has developed a label-free tomographic method for measuring and reconstructing 3D dielectric tensors, which have not been directly measured thus far. ...read more
-
Research Highlight
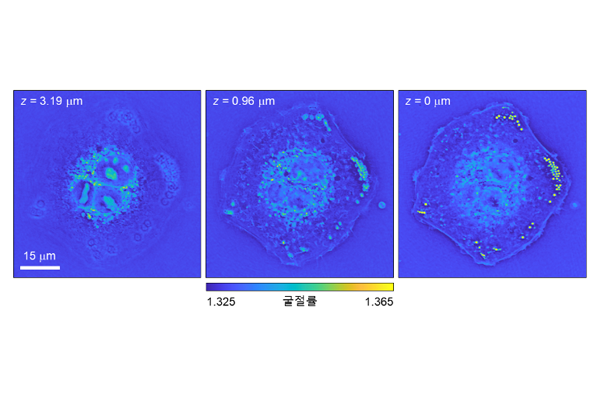
New holographic microscopy enables the 3D label-free imaging of biological specimens without interferometry
Prof. YongKeun Park’s group has developed a novel microscopy technique for the label-free imaging of biological specimens. Based on Kramers-Kronig relations, this new method produces quantitative phase images of biological specimens with an optical microscope simply by controlling the incident angle of illumination....read more
-
Research Highlight
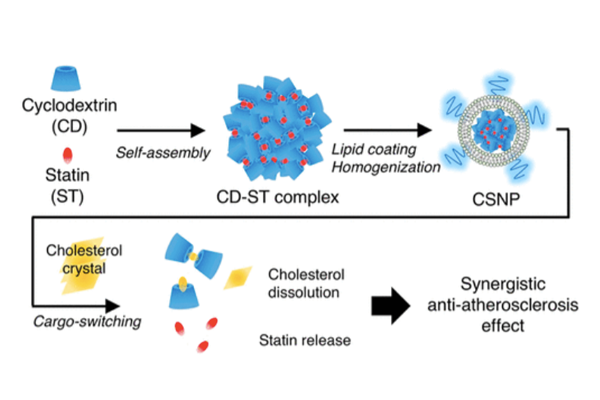
New Nanoparticle Drug Combination Treats and Prevents Atherosclerosis
Dr. Ji-Ho Park’s group developed a cargo-switching nanoparticle (CSNP) system that can bind to cholesterol and then release an anti-inflammatory drug (statin) in a plaque-containing microenvironment. The as-developed CSNP had a core-shell structure, with a core composed of cyclodextrin and statin and a shell of phospholipids. In vitro, once interacting with cholesterol, which had a higher affinity to cyclodextrin than statin, the CSNP can instantly release statin and scavenge cholesterol by cargo-switching. In vivo, in a mouse model of atherosclerosis, the CSNP administered systemically can effectively target atherosclerotic plaques and reduce their associated cholesterol and macrophages, leading to prevention of atherogenesis and regression of established plaques....read more

291 Daehak-ro Yuseong-gu Daejeon, 34141, Republic of Korea
Partnered with KAIST Breakthroughs and KAIST Compass