-
Research Highlight
Efficient Exploration of Multimetallic Alloys for Optimal Bifunctional Catalysts in Water Splitting through Pareto Active Learning and Experiments
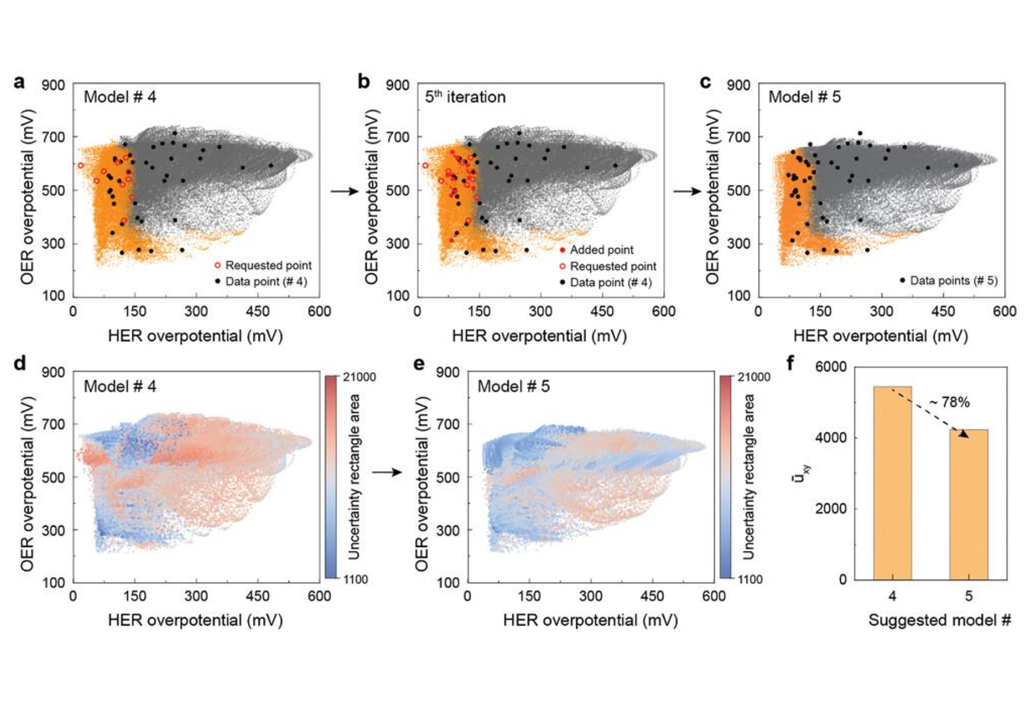
A study published by Prof. Hee-Tae Jung’s group on the efficient production of renewable energy through the search for optimal bifunctional multimetallic alloy catalysts has shown promising results. The study used a Pareto active learning framework and carbothermal shock method for nanoparticle synthesis to efficiently determine optimal metallic compositions for bifunctional catalysts of up to four component elements for electrocatalytic reactions. The approach can be extended to different catalytic reaction fields and other multifunctional applications....read more
-
Research Highlight Top Story
Selective and Efficient Photocatalytic Conversion of CO2 with Ultrathin Nanosheets
Prof. Doh Chang Lee’s group has developed a novel photocatalyst based on ultrathin CdS nanosheets for selective and efficient light-driven conversion of CO2 into CO. Surface engineering at atomic precision on CdS nanosheets enabled spatial separation of the reductive active sites and the oxidative active sites to designated facets. The facet-resolved redox-active sites favored efficient charge separation in the CdS nanosheets under light, leading to two-orders-of-magnitude increase in conversion rate of CO2-to-CO. ...read more
-
Research Highlight
Nanowrinkled Copper Catalyst via Graphene Growth for Carbon Dioxide Conversion into Ethanol
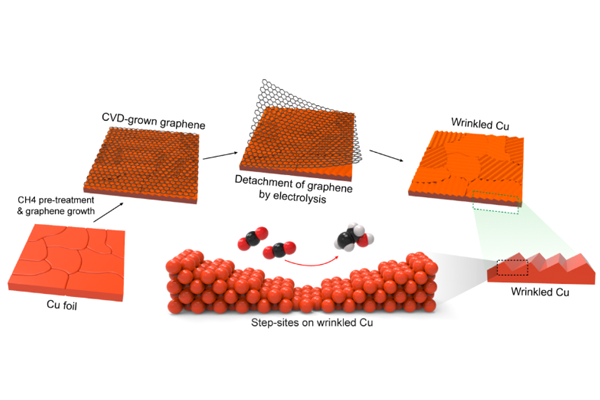
Prof. Hee-Tae Jung’s group has reported high conversion of CO2 into ethanol by synthesizing a wrinkled Cu catalyst with high facets via a graphene growth process....read more
-
Research Highlight Top Story
Fiber Sorbents for Energy-Efficient CO2 Capture
Prof. Koh’s group conceived a feasible route for developing a scalable platform for CO2 capture (including direct air capture) using metal-organic frameworks. MOF-based fiber sorbents show high CO2 uptake and low pressure drop for long-term cyclic operation in direct air capture mode....read more
-
Research Highlight
Accelerated Material Design Framework using Uncertainty-Quantified Hybrid Machine Learning/Density Functional Theory Approach
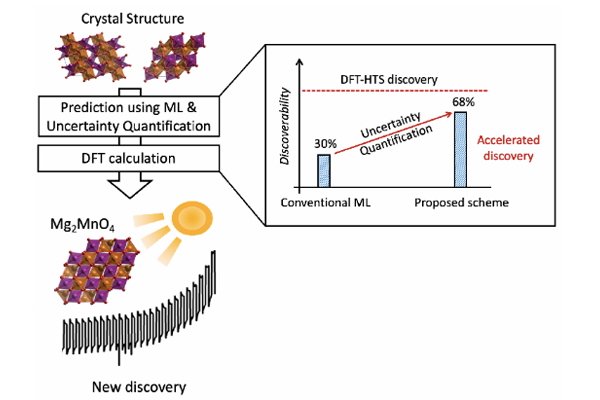
Prof. Yousung Jung’s group has developed a new accelerated high throughput screening (HTS) method using uncertainty-quantified machine learning (ML) and density functional theory (DFT) that was applied to explore the Mg-Mn-O chemical space for photoanode application. Notably, the proposed HTS scheme required only 1.5% of the target chemical space for further DFT calculations, accelerating the entire process by > 50 times for the same discovery compared to the brute-force DFT-HTS done previously. This means an improvement of the screening performance (discoverability) by more than a factor of 2 compared to the conventional ML-based HTS approach....read more
-
Research Highlight Top Story
New Catalyst Recycles Greenhouse Gases into Fuel and Hydrogen Gas
Prof. Yavuz’s group has developed a new catalyst for dry reforming of methane. The catalyst exhibits outstanding stability and activity without deactivation, attributed to the migration of Ni-Mo nanocrystals to the edge of single crystal MgO....read more
-
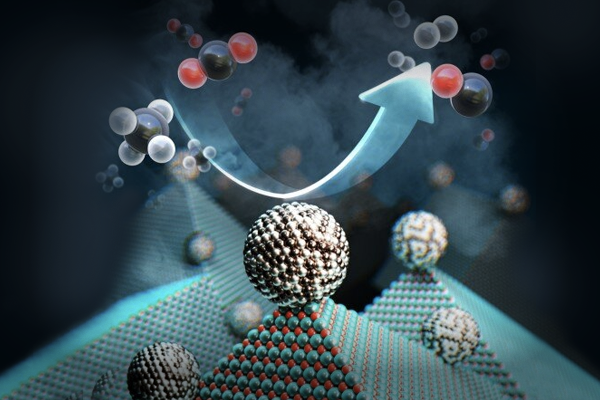
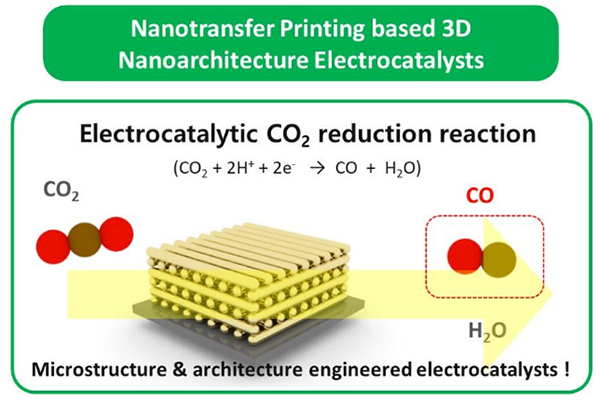
Research Highlight
3-Dimensional Catalysts Facilitate Conversion of CO2 into Useful Fuels
KAIST team developed multi-stacked 3-dimensional Au catalyst architecture to enhance the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction....read more
-
Research Highlight
Morphology Analysis of Solution-Sheared Halide Perovskite Film
A technique known as solution-shearing has been utilized to generate a thin film of perovskite CH3NH3PbI3 over a large area in a facile and cost-effective manner...read more
-
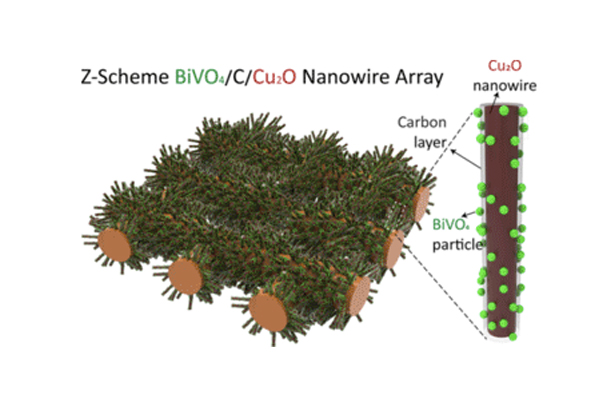
Research Highlight
Three-Dimensional Nanostructured Z-scheme Photocatalyst for Carbon Dioxide Conversion
Efficient and stable CO2 conversion under visible light by using a novel photocatalyst with Z-scheme charge flow on 3-dimensional nanowire arrays....read more
-
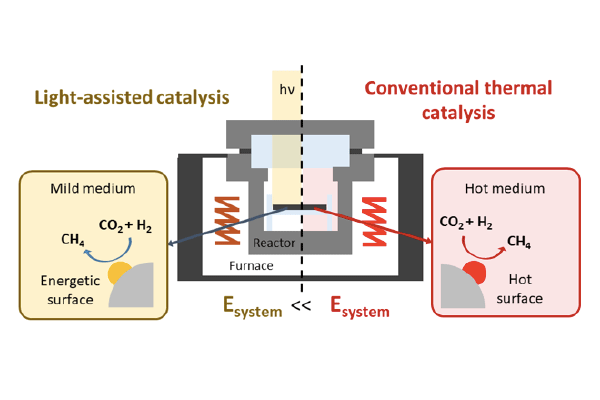
Research Highlight
Energy-Saving CO2 Hydrogenation Using Light
Light-assisted CO2 hydrogenation produced methane on a Ru/SiO2 catalyst. By using both light and heat as an energy source, the total energy required for CO2 conversion could be reduced to 37%. The chemical reaction can be easily initiated or terminated by simply turning on or off the light....read more

291 Daehak-ro Yuseong-gu Daejeon, 34141, Republic of Korea
Partnered with KAIST Breakthroughs and KAIST Compass