-
Research Highlight
AI for Social Good Summit: Mobilizing Artificial Intelligence for Maternal Health in Bangladesh
KPC4IR’s Dr. Cornelius Kalenzi presented a paper at the AI for Social Good Summit, which brought together academics and government representatives to showcase joint research outcomes to enhance well-being in Southeast Asia...read more
-
Research Highlight
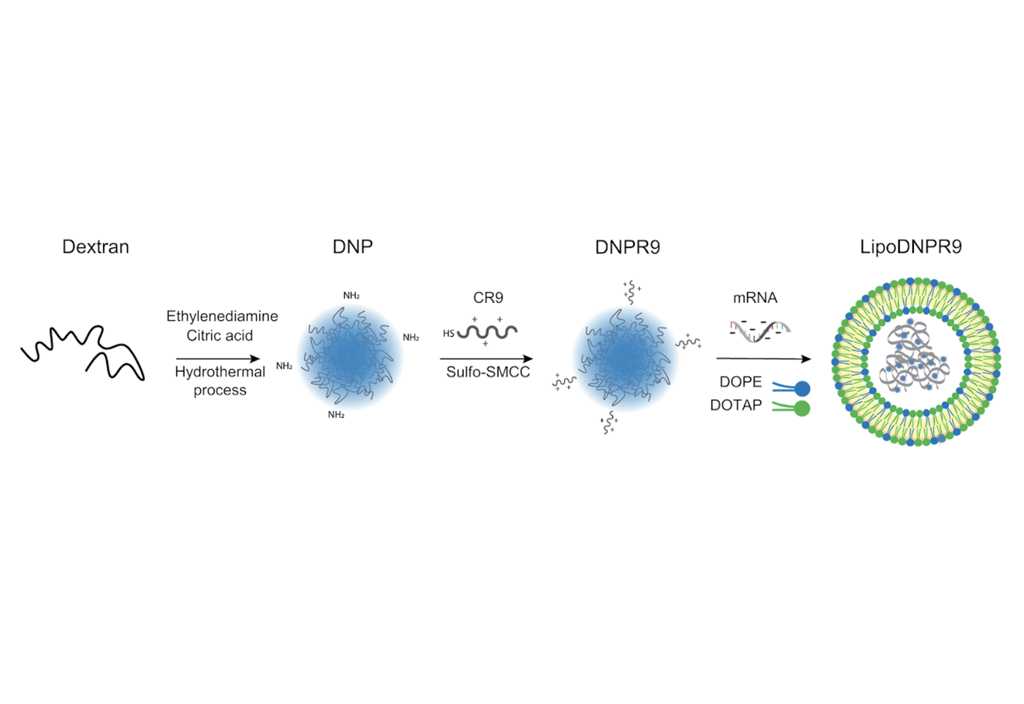
Effective mRNA Delivery by Condensation with Cationic Nanogels Incorporated into Liposomes
Prof. Chung’s group has developed an mRNA delivery system using cationic nanogels as a condensing material for mRNA and a lipid-based nano-formulation. ...read more
-
Research Highlight
Sex-specific effects of social isolation on shaping social behavior and maturing cortical neurons during adolescence
Prof. Lee’s group found adolescent social isolation dampens sociability and cortical maturation only in female mice. They performed anatomical, physiological, behavioral, genetic knock-out, and optogenetic studies to prove that the expression of a specific gene, parvalbumin, in GABAergic neurons is important for shaping sociability in female mice....read more
-
Research Highlight
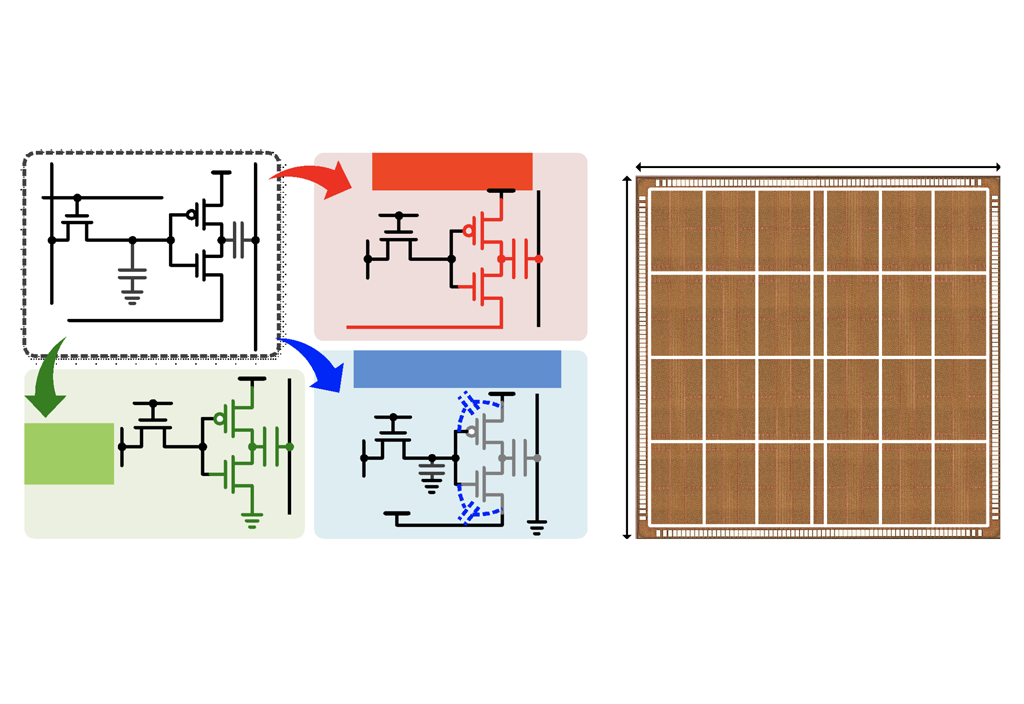
An eDRAM In-Memory-Computing-Based Reconfigurable Spatial Accelerator with Triple-Mode Cell for Dynamic Resource Switching
A research team led by Prof. Yoo at KAIST ITC has developed DynaPlasia, an in-memory computing (IMC) semiconductor that performs artificial intelligence operations by integrating a computing logic directly inside a DRAM memory cell....read more
-
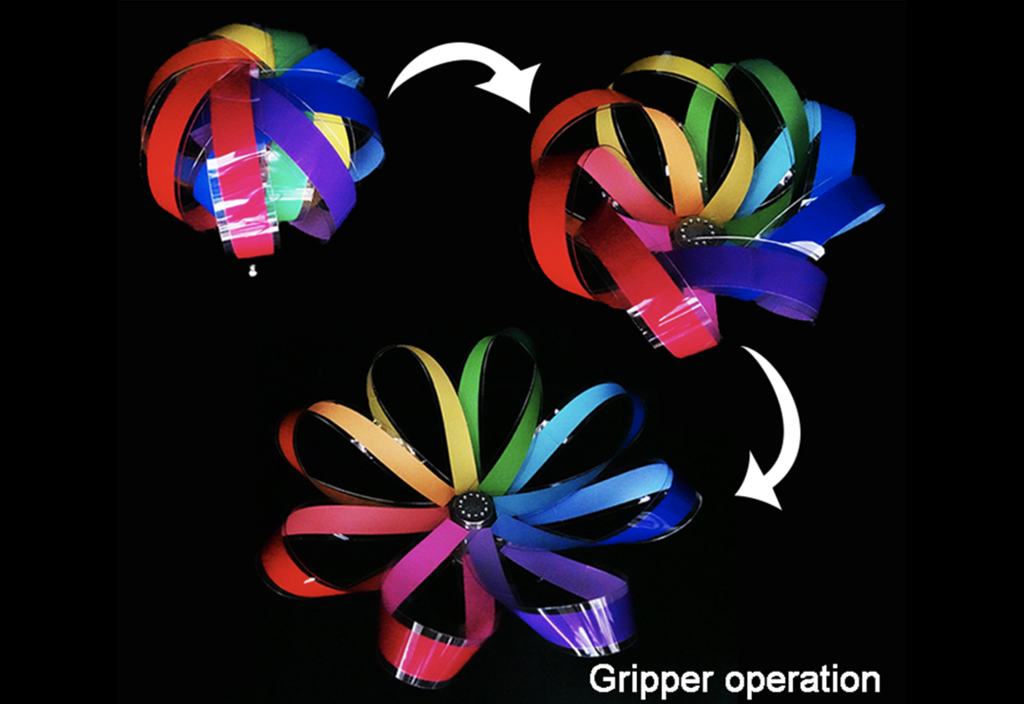
Research Highlight
Ultra-strong soft gripper that lifts 100kg with 130g
Prof. Lee’s group, in collaboration with KIST, innovated a lightweight, cost-effective soft robotic gripper capable of securely holding 100kg objects, promising enhanced utility in various domestic and industrial applications....read more
-
Research Highlight
2.5D Laser-Cutting-Based Customized Fabrication of Long-Term Wearable Textile sEMG Sensor
Prof. Jung Kim’s group has developed a 2.5D laser cutting method to accelerate customized sEMG sensor fabrication from design to production. sEMG sensors measure human muscle activity and are widely used in wearable systems for human-machine interaction. In order to use sEMG sensors for a long time in daily life, it is necessary to develop a sensor that can be customized and worn easily and does not affect the signal due to movement. This customizable textile-based sEMG sensor provides high wearing comfort and improves the sensor signal quality through stable contact....read more
-
Research Highlight
A new toughening strategy for self-healing polymer
Prof. Kang’s group has developed a new toughening strategy for self-healing polymers crosslinked by metal–ligand coordination using mixed counter anion dynamics. This strategy concurrently and significantly enhances their mechanical toughness and self-healing efficiency....read more
-
Research Highlight Top Story
Human muscle-inspired Hercules artificial muscle fiber
Prof. Sang Ouk Kim’s group has developed robust and durable actuator fibers by incorporating 2D graphene fillers in aligned liquid crystal elastomer matrix; these fibers surpass the strength and toughness of human muscle. The reversible percolation of the graphene filler network within the composite structure upon contraction/recovery actuation offers interesting electrical switching behavior, as well as work capacity and power density far beyond those of human or mammalian muscles....read more
-
Research Highlight
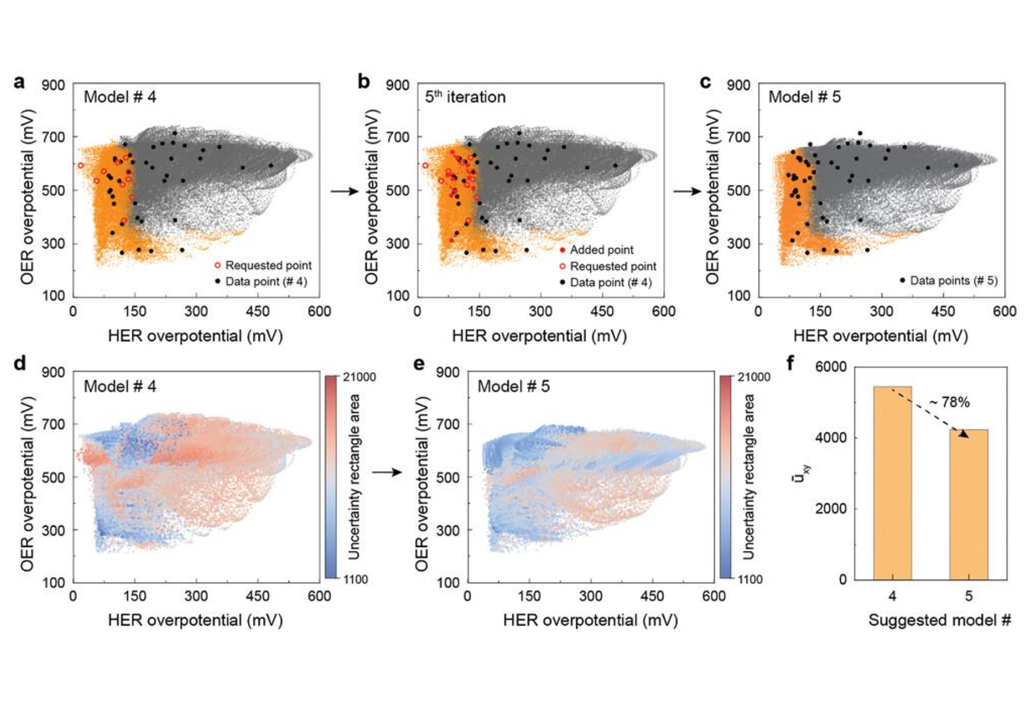
Efficient Exploration of Multimetallic Alloys for Optimal Bifunctional Catalysts in Water Splitting through Pareto Active Learning and Experiments
A study published by Prof. Hee-Tae Jung’s group on the efficient production of renewable energy through the search for optimal bifunctional multimetallic alloy catalysts has shown promising results. The study used a Pareto active learning framework and carbothermal shock method for nanoparticle synthesis to efficiently determine optimal metallic compositions for bifunctional catalysts of up to four component elements for electrocatalytic reactions. The approach can be extended to different catalytic reaction fields and other multifunctional applications....read more
-
Research Highlight
Semiconductor Design Research for Artificial Intelligence (AI)
PIM is an abbreviation of Processing In Memory and is a kind of future semiconductor memory architecture. It makes it possible for memory and logic processing to operate together with higher speed and less energy consumption. In this bulletin, the three major activities of PIM-SDRC and its achievements are briefly introduced. The center will carry out key roles in building a PIM IP hub, making the infrastructure design service and relevant IP business, and training competent design manpower....read more

291 Daehak-ro Yuseong-gu Daejeon, 34141, Republic of Korea
Partnered with KAIST Breakthroughs and KAIST Compass